How to Use the Colour Wheel to Choose the Best Colour Palette for Any Room
You can use this easy-to-use tool to find colour combos that look good together.
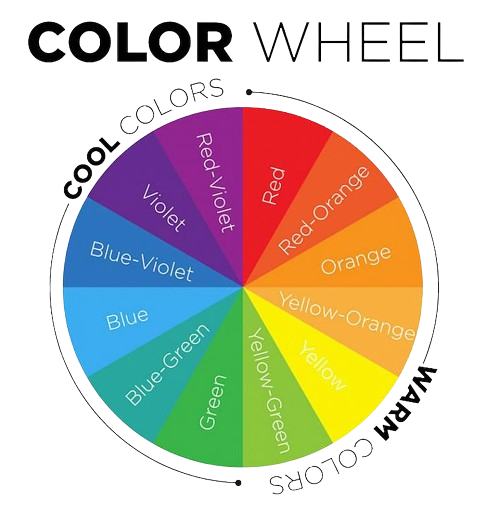
The colour wheel is an easy way to choose paint colours and see which colours go well with each other. The wheel is a diagram that shows how the colours of the rainbow fit together to make every colour combo you can think of. The colour wheel divides the spectrum into 12 basic hues: three primary colours, three secondary colours, and six tertiary colours. This makes it easy to see how colours relate to each other. The colour wheel theory and its many possible combos can help you choose which colours to use in your home once you know how to use it.
How the Colour Wheel Works
There are 12 parts to a colour wheel, and each one stands for a colour. Third-level colours are made up of three main colours, three secondary colours, and six tertiary colours.
Red, blue, and yellow are the main colours. You can’t make these colours from other colours because they are pure. All other colours are made from these.
Orange, green, and purple are secondary colours. You can find these colours between the primary colours on the colour wheel. This is because they are made by mixing equal parts of two basic colours.
When you mix a primary colour with the secondary colour next to it on the colour wheel, you get a tertiary colour. Each time the colours are mixed (primary with primary, then primary with secondary), they become less bright. These are some tertiary colours:
- Red-orange
- Yellow-orange
- Yellow-green
- Blue-green
- Blue-violet
- Red-violet

You can create colour schemes by using the colour wheel
The segments on the colour wheel can help you mix colours and make schemes with different levels of contrast. The colour wheel can be used to make four popular types of colour schemes.
Monochromatic Colour Scheme

Tone-on-tone monotone colour schemes use a soft palette made up of different shades (by adding black) and tints (by adding white) of the same colour. Blues like sky blue, pale blue, and navy come to mind. Use a range of colours and textures to make a one-colour scheme work. This will help the room stand out. The colour pink in a bedroom stays close to the pink wedge on the colour wheel, but there are different shades that run from blush to rosy.
You could also add small items to give the outfit a greater pop. Finally, a knit throw and a weaving rug break up the simple colour scheme with different textures.
Analogous Colour Scheme

Analogous palettes use contrast and colours that are next to each other on the colour wheel, like orange, yellow, and green, to create a lively but calm atmosphere. The base colours of colours that are close to each other work well together.
One colour should be the main one in a room. Then pick one, two, or three colours to use as accents. In a similar colour scheme of blue, purple, and fuchsia, a dusty purple sofa could be the main colour, with bright fuchsia showing up on the throw pillows and in the flower arrangement. The purple tones in the pink and blue accents go well with the colour wheel pattern. The room is finished off with warm grey walls.
Complementary Colour Scheme

Using two colours that are opposite each other on the colour wheel, like orange and blue, will always make a room feel more alive. The way these colours balance each other out makes them look good together. A deep cobalt blue looks good with a bright orange colour because it adds warmth and brightness. It’s important not to let one colour take over the other. As the wall colour, blue stands out more, and orange is used as an accent. For a unified look, the two colours are used on other things in the room.
Triadic Colour Scheme

Using three colours that are evenly spread on the colour wheel, like turquoise, fuchsia, and yellow-orange, makes a triad. This mix of colours makes a colour scheme with strong contrasts and well-balanced colours. These bright plans work well because they make people feel happy and energised. To make contrast or tone down the brightness, use the three colours in different shades and tints. A living room might have strong shades of orange and green, along with a hint of a third colour, like a bland pastel couch.
Warm and Cool Colours
Colours can make you feel different emotions and set a mood. Yellows are energising and make you feel good, while greens tend to calm you down. People think of bold reds as passionate and brave, while soft pink, which is a tint of red, is seen as sweet and gentle. People think of blues as peaceful and calm, oranges as warm and cosy, and purple, which is a very complicated colour, as either sexy or spiritual.
People think of colours as nice or cool because of the memories they bring up. Colours that are cool are blue, green, and violet. Colours that are warm are red, orange, and yellow. Warm colours make us think of fire and the sun, while cool colours make us think of water, the sky, and plants. If you want your colour scheme to look balanced, don’t just use warm or cool colours. Let one stand out and set the mood for the room as a whole, but add things that are different to keep things interesting.
Colour Wheel Terminology
You can use this list of colour wheel terms to help you choose colours for your home.
Analogous: colours that are close to each other on the colour wheel, like orange, yellow-orange, and yellow.

Chroma is the brightness or darkness of a colour.
The complementary shades of each other on the colour wheel that look better when used together (yellow and purple, red and green, blue and orange).

Neutral: Black, white, brown, and grey are all neutral colours. These colours are soothing because they are not very bright or saturated.
Secondary: a mix of two main colours in equal amounts (green, orange, and purple are secondary colours).

Shade is any colour that has black added to it. It can also mean small changes in a colour.
Red, yellow, and blue are the primary colours. They are the only colours that can be mixed to make any other colour on the wheel.

Split complementary means that two colours that are very similar to each other are grouped together, like yellow with red-violet and blue violet.

A triad is any three colours that are evenly spread on the colour wheel. In a colour scheme, one of the triad colours usually stands out more than the others.
Tertiary colours are made up of equal amounts of a primary colour and a secondary colour. These colours are red-orange, yellow-orange, yellow-green, blue-green, blue-violet, and red-violet.

Any colour with white added to it is called tint.
Tone is the level of brightness or darkness of a colour.









Comment (1)
[…] you’re doing a deeper palette, a slightly tinted ceiling (not brilliant white) makes the room feel wrapped and […]
Comments are closed.